Ms Access Subquery syntax is the Select statement inside the Select query statement or in select statement used to select and display even more specific data, since sub-queries can look up tables that are not in the main query, they are very useful for filtering forms and reports.
The syntax for the subquery:
• [ANY | ALL | SOME]
• [NOT] IN
• [NOT] EXISTS
[ANY | ALL | SOME]: Choose one of the value. The [ANY | ALL | SOME] is used to retrieve records in the main query that satisfy the comparison with any records retrieved in the subquery
[NOT] IN: is to retrieve only those records in the main query for which some record in the subquery contains an equal value. [NOT] is optional, if used will reverse the result.
[NOT] EXISTS: is to determine whether the subquery returns any records in true/false comparisons. [NOT] is optional, if used will reverse the result.
NOTE: those syntaxes are followed by other SQL statements.
Example in IN:

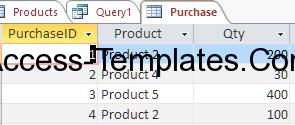
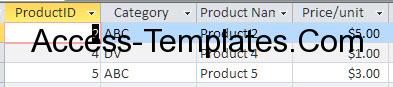
There are 2 tables, the upper one is the Products table, while the other one is Purchase table. With these tables, we will create a query to show the Purchase records where the Product Category is “ABC”.
Go to Create tab > Query Design. Select the view into SQL mode. Then input the syntax:
SELECT * FROM Purchase
WHERE Product IN
(SELECT ProductID FROM Products
WHERE Category=”ABC”);
If it done right, it will show like this picture:

Example in EXISTS:
Remember that the Exists is for comparing. So, we will create the query that show the records of what are the product sold
SELECT * FROM Products a WHERE EXISTS (
SELECT * FROM Purchase b where b.Product = a.ProductID)
Result:

It is more recommended to write the Subquery statement in SQL Query mode or VBA code for neater look and code. However, you can use it in Query Design. In Query Design, go to Property box and in Criteria row, input the syntax. However, only type the syntax started from the subquery syntax, not from the first SELECT statement.
Example in ANY:
SELECT * FROM Purchase
WHERE Product = ANY
(SELECT ProductID FROM Products
WHERE Category=”ABC”);
The result will be same with example in IN.